The Sandbox is a scalable cloud computing environment internal to ONC that enables users to upload and run their scripts (programs using Oceans 3.0 data) on ONC servers that are "closer" to the data. This enables faster and more efficient data access which is particularly important with high-volume data such as acoustic or video data. Programs can be written in any of several languages including C/C++, Python, Matlab, or R, and can be either scheduled or ad hoc. The Sandbox contains the Oceans 3.0 client libraries pre-installed, as well as other commonly used libraries such as the scipy/numpy scientific computing stack in Python. This set of libraries enables users to perform their desired scientific computing operations simply by calling the appropriate functions in their scripts.
The Sandbox can be accessed by logging in to Oceans 3.0 and selecting "Task Management" from the "More" menu, at data.oceannetworks.ca, or directly at data.oceannetworks.ca/TaskManagement.
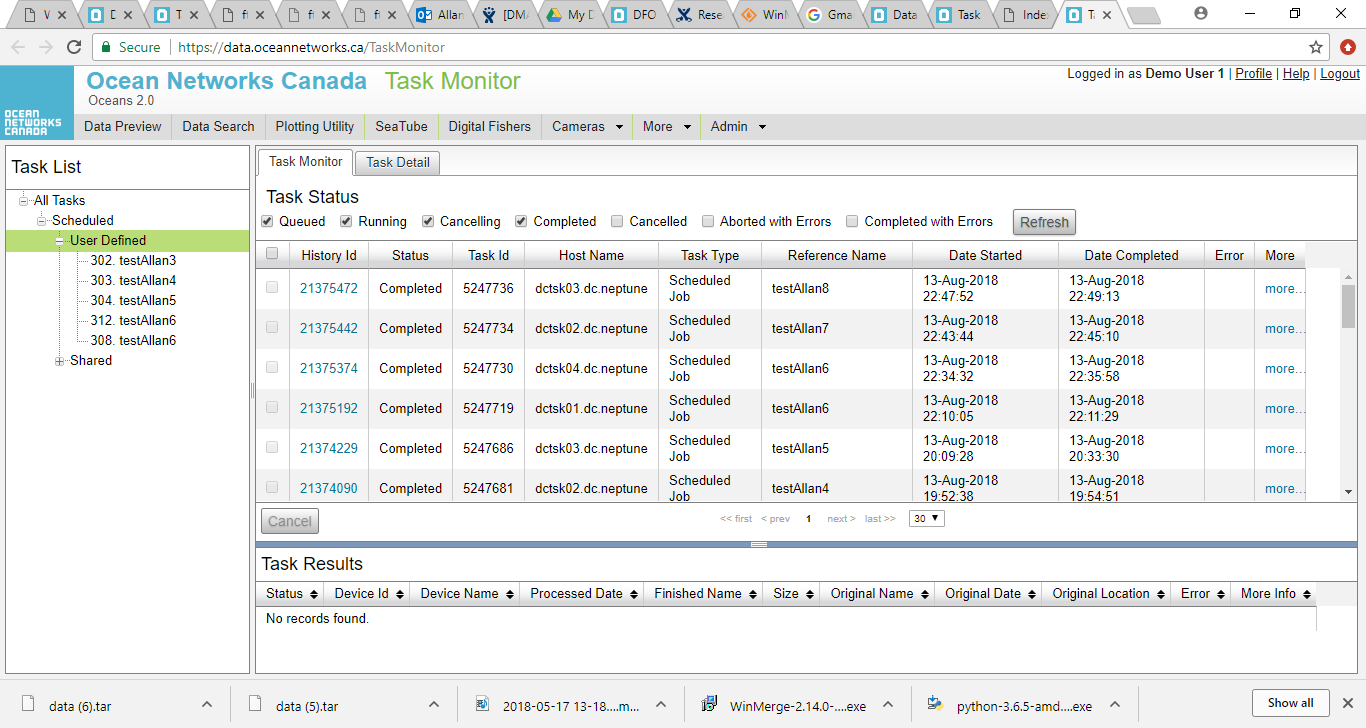
The Sandbox is accessed through a web interface shown in the figures below. The Task Monitor tab shows a list of tasks and their status, while the Task Detail tab enables the addition of new tasks. This interface enables the user to upload either a script (computer program) or a Docker file containing a compiled version of a program. Docker is a system that allows users to create programs in their own programming languages and compile them to a common format that can be safely run in an environment like the Sandbox. This opens up the ability to use the API to any programming language in which web service calls can be made, which can be compiled to Docker images. Docker employs the use of containers around programs that protect the environment from the program and vice versa, so that any erroneous operation of a program will not damage the environment or other programs that might be running concurrently.
One example of an operation that is much more efficient in the Sandbox than in other computing environments is the processing of hydrophone data. This type of data has a high sampling rate and is collected continuously over time. This time-series data is often converted into frequency data through the use of a Fourier Transform, typically with a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm. For best results it is often necessary to use large amounts of time-series data as more data results in more accurate determination of the frequencies in a signal, and therefore better scientific results from the use of that data.
Videos demonstrating the use of the Sandbox can be seen at: http://www.oceannetworks.ca/dfo-sandbox
The Sandbox enables users to either run their scripts directly and obtain the output, or to schedule them for later or recurrent processing. Users can monitor the status of multiple scheduled jobs.
User management in the Sandbox enables users to have their own personal space in which to run scripts, and their own file directories in which to store results or intermediate files, which can be accessed by FTP. These directories are meant for temporary use, and users should download their files and delete them from the FTP directory when they are no longer needed. Generated files are purged two weeks after the run.
In future updates to the Sandbox system users will have the ability to link together different scripts to perform more complex operations.
Sandbox Design: